Basic Components - Optocouplers
An optocoupler is a device that integrates a light-emitting diode (LED) and a photodetector into a single package.
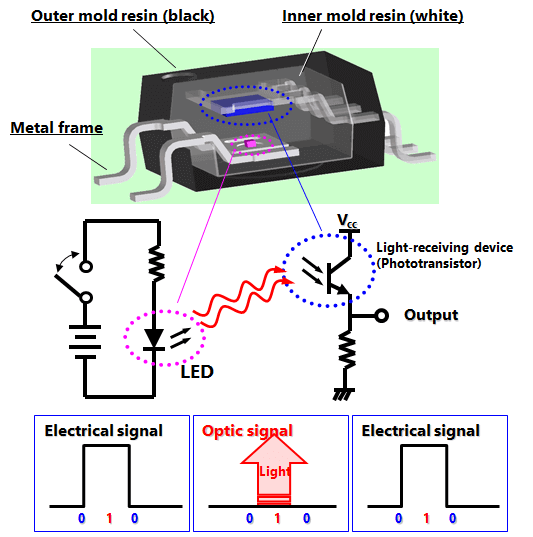
Function of Optocouplers
In an optocoupler, the primary side (LED side) and the secondary side (light-receiving device side) are electrically isolated. This means that even when the electrical potentials of the primary and secondary sides (including the ground potential) are different, a signal on the primary side can be transmitted to the secondary side. Optocouplers effectively isolate the two circuits.
References and Acknowledgments
- Discrete Semiconductor Devices - Chapter V: Optoelectronics
- Optocoupler Parameters and Their Significance
Original: https://wiki-power.com/ This post is protected by CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 agreement, should be reproduced with attribution.
Parameters of Optocouplers
LED Side:
- Forward Voltage (Vf): Vf refers to the voltage drop across the LED at a given operating current. Common low-power LEDs are typically tested with If=20mA to determine the forward voltage. Different LEDs may have different testing conditions and results.
- Reverse Voltage (Vr): This is the maximum reverse voltage that the LED can withstand. Exceeding this reverse voltage may damage the LED. When driving LEDs with AC pulse signals, it is important not to exceed the reverse voltage.
- Reverse Current (Ir): Usually, this refers to the reverse current flowing through the LED under the maximum reverse voltage conditions.
- Maximum Power Dissipation (Pd): This is the maximum power that the LED can handle. Exceeding this power dissipation may damage the LED.
- Peak Wavelength (λp): It represents the central wavelength of the light emitted by the LED. The wavelength directly determines the color of the light. Multi-color LEDs may have several different central wavelength values.
- Forward Current (If): If is the forward current that flows through the LED during normal illumination. Different LEDs have varying maximum allowable current.
- Peak Forward Current (Ifp): Ifp is the peak forward current flowing through the LED. To ensure a longer lifespan, LEDs are often driven with pulse signals. The Ifp specified in the LED datasheet is usually calculated with a 0.1ms pulse width and a 1/10 duty cycle.
Phototransistor Side:
- Collector Current (Ic): The current flowing through the collector of the phototransistor, typically representing its maximum value.
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vceo): The maximum voltage that the collector-emitter junction of the phototransistor can withstand.
- Emitter-Collector Voltage (Veco): The maximum voltage that the emitter-collector junction can withstand.
- Reverse Saturation Current (Iceo)
- C-E Saturation Voltage (Vce(sat))
Transfer Characteristics:
- Current Transfer Ratio (CTR): Usually expressed in terms of direct current transfer ratio. When the output voltage remains constant, CTR is the percentage of direct current output (IC) to direct current input (IF).
Isolation Characteristics:
- Input-Output Isolation Voltage (Vio): The withstand voltage value between the input and output of the optocoupler.
- Input-Output Isolation Capacitance (Cio): The capacitance between the input and output of the optocoupler.
- Input-Output Isolation Resistance (Rio): The insulation resistance value between the input and output of the semiconductor optocoupler.
This post is translated using ChatGPT, please feedback if any omissions.