HAL Library Development Notes - DMA
DMA (Direct Memory Access) allows hardware devices of different speeds to communicate directly, without relying on a heavy load of interrupts from the CPU.
Basic Principles
What is DMA
DMA provides high-speed data transfer between peripherals/memory or memory/memory without occupying CPU resources.
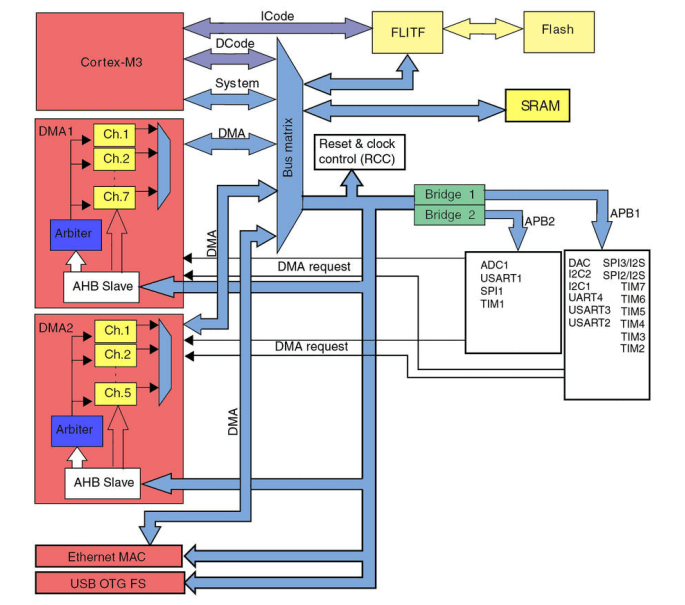
As shown in the diagram above, the STM32F4 series has two DMA controllers with a total of 12 channels (7 in DMA1 and 5 in DMA2). The DMA controllers share the system's data bus with the Cortex-M3 core.
In simple terms, when the CPU doesn't want to bother moving a large amount of data to another location, or when it has more important tasks to handle, it can delegate this task to DMA. DMA completes the task, and if any issues arise, it informs the CPU.
Use Cases for DMA
- Serial Communication: The most common use case is when there's a significant amount of data to be read from or written to a serial port. In such situations, DMA can handle the data transfer, freeing up the CPU for more critical tasks.
- ADC (Analog-to-Digital Conversion): In channel scanning mode when ADC is required, DMA can be used.
- SD Card Read/Write: When a substantial amount of data needs to be read from or written to an SD card, DMA is typically employed.
DMA Transfer Directions
- P2P (Peripheral to Peripheral).
- P2M (Peripheral to Memory): This is often used when sensors send readings to a microcontroller via a serial port.
- M2P (Memory to Peripheral): It's generally used when a microcontroller needs to send data to actuators via a serial port.
- M2M (Memory to Memory): This is used for data transfers within the MCU, commonly seen when data needs to be transferred between buffers or when reading and writing data from/to buffers. Only DMA2 can perform M2M operations.
DMA Transfer Modes
- DMA_Mode_Normal: Normal mode. DMA stops after completing the task and needs to be manually restarted if further transfers are required.
- DMA_Mode_Circular: Circular transfer mode. When a transfer is completed, the hardware automatically reloads the data transfer quantity register for the next round of data transfer.
Common DMA Function References
Sending Data via UART with DMA
Function: Send data of a specified length through UART using DMA.
Parameters:
- UART_HandleTypeDef *huart: The UART handle (e.g., UART_HandleTypeDef huart1 -> huart1).
- *pData: The data to be sent.
- Size: The number of bytes to send.
Example:
HAL_UART_Transmit_DMA(&huart1, (uint8_t *)Senbuff, sizeof(Senbuff)); // Send the Senbuff array via UART
Receiving Data via UART with DMA
Function: Receive data of a specified length through UART using DMA.
Parameters:
- UART_HandleTypeDef *huart: The UART handle (e.g., UART_HandleTypeDef huart1 -> huart1).
- *pData: An array to store the received data.
- Size: The number of bytes to receive.
Example:
HAL_UART_Receive_DMA(&huart1, (uint8_t *)Recbuff, sizeof(Recbuff)); // Receive data via UART and store it in the Recbuff array
UART DMA Resume Function
Function: Resume DMA transfer Return Value: 0 (Resuming) ; 1 (Resumed)
DMA Serial Transmission Experiment
Configuring DMA in CubeMX
For the configuration of the UART section, please refer to the article HAL Library Development Notes - Serial Communication.
After configuring the USART pins and NVIC interrupts, switch to the DMA Settings tab and configure as shown in the following image:
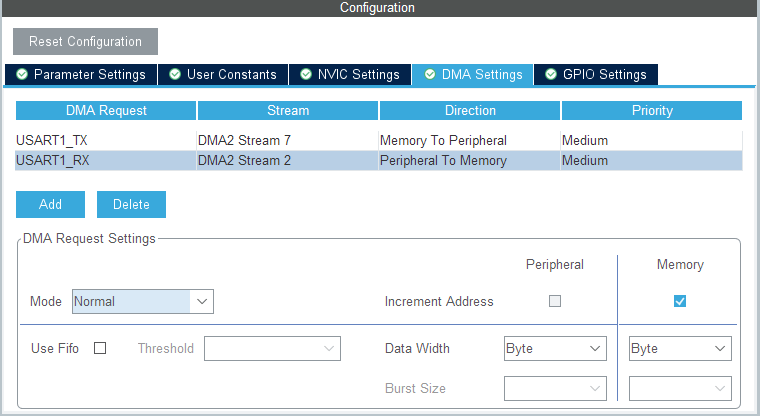
- Click
Addto add channels (USART1_RX and USART1_TX). - Set the priority of both channels to
Medium. - Set DMA transfer mode to
Normal. - DMA memory address increments by one byte.
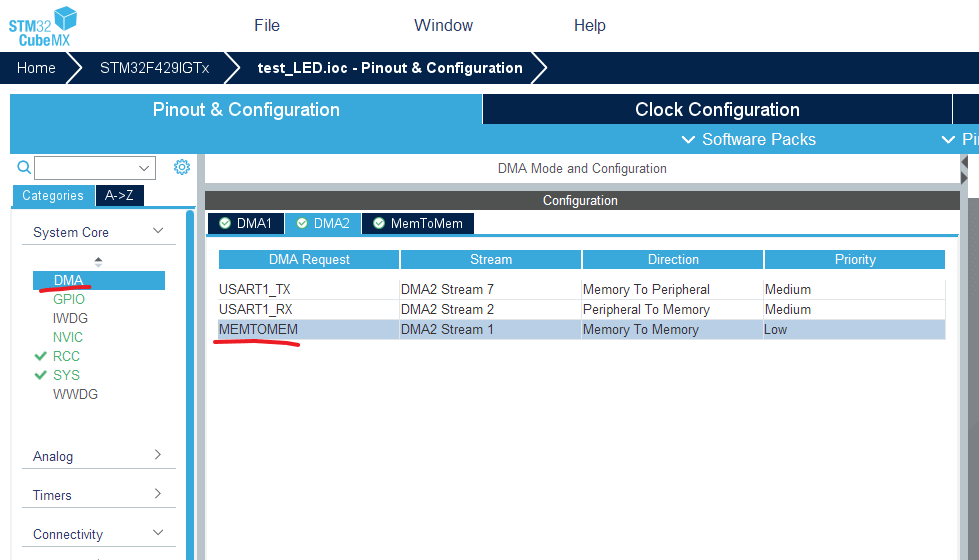
Next, in the System Core tab, locate DMA and add a MEMTOMEM item as shown below:
Configuring DMA in the Code
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
uint8_t SendBuffer[] = "Serial Output Message by DMA \r\n"; // Custom string to be sent
/* USER CODE END Init */
......
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
HAL_UART_Transmit_DMA(&huart1, (uint8_t *)SendBuffer, sizeof(SendBuffer));
HAL_Delay(1000);
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
Flash the program, open a serial assistant, and you will see the custom array being sent in a loop.
References and Acknowledgments
- Advanced Guide IV [DMA]
- 【STM32】HAL Library STM32CubeMX Tutorial Eleven - DMA (UART DMA Transmit/Receive)
Original: https://wiki-power.com/
This post is protected by CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 agreement, should be reproduced with attribution.